4.2 KiB
Git Assignment
1. What is Git and Version Control
What problem does Git solve? Git tracks changes in files (especially code) and helps multiple people collaborate without overwriting each other’s work. It lets you save versions, go back if something breaks, and merge changes safely.
Real-life example: A school group project where everyone writes different parts of the same report. Git combines everyone’s edits into one final version without losing work.
Why is Git better than emailing files? Emailing creates many confusing copies (e.g., report_final.docx, report_final2.docx). Git keeps a single version, records who changed what, and merges edits automatically, making collaboration easier and safer.
Git Version Check
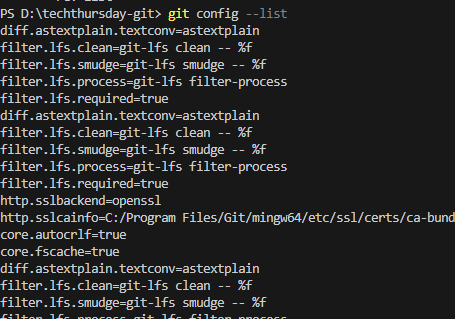
2. Installing Git & Configuring User Info
Git List
3. Initializing a Repository
Git Init
4. Working Directory, Staging, and Commits
Git Add
5. Adding & Committing Files
Git Log
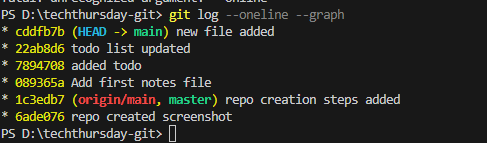
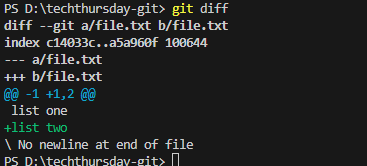
6. Viewing Commit Logs & Diffs
Git Log (graph)
Git Diff
Git Diff (commit1 vs commit2)
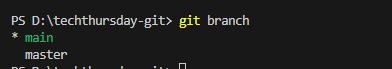
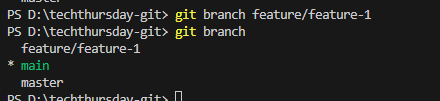
7. Creating & Switching Branches
Git Branch
8. Cloning a Remote Repository
Git Clone
9. Adding & Managing Remotes
Git Remote
10. Pushing & Pulling Changes
Git Pull
Git Push
11. Ignoring Files with .gitignore
.gitignore
Part 1: Viewing File History
git log -- filename.extension
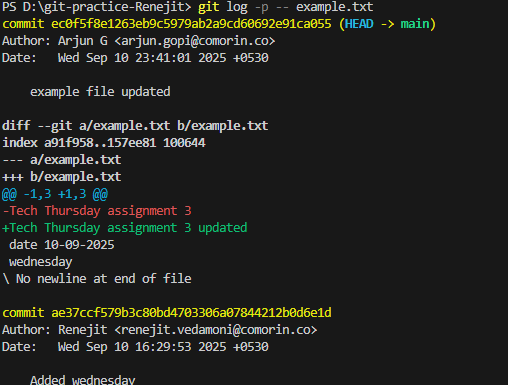
git log -p -- filename.extension
git log --oneline -- filename.extension
How many commits modified this file? 3
What differences do you see when adding the -p option? It describes what changed — which lines were added (+), which lines were removed (−)
Part 2: Viewing File History with Blame
git blame -- filename.extension
git blame -L 1,5 -- filename.extension
git blame -e -- filename.extension
Who changed each line of the file? Arjun,Renejit, Arjun, Arjun ec0f5f8e (Arjun G 2025-09-10 23:41:01 +0530 1) Tech Thursday assignment 3 updated ae37ccf5 (Renejit 2025-09-10 16:29:53 +0530 2) date 10-09-2025 f97b76b3 (Arjun G 2025-09-11 00:00:58 +0530 3) wednesday dc7fc330 (Arjun G 2025-09-11 00:01:50 +0530 4) Practise session extended to Thursday
How does -L help when the file is large? Limits the blame output to just a range of lines when the file is large.
What extra information does -e provide? Author email
Part 3: Merging Branches
git checkout -b feature/feature-1
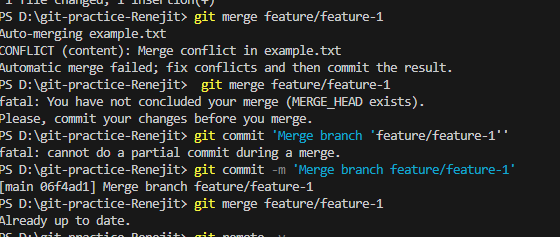
git merge feature/feature-1
git log --graph --oneline --all
Did Git perform a fast-forward merge or a 3-way merge? 3 way merge
What does git log --graph --oneline --all show after the merge? shows a merge commit (06f4ad1) at the top. The graph shows two diverging branches (main & feature/feature-1) and how they were joined together. main now contains all changes from both histories.